104. Maximum Depth Of Binary Tree
14 Jul 2024
104. Maximum Depth Of Binary Tree (Easy) 栈的最大深度
题干
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree’s maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:
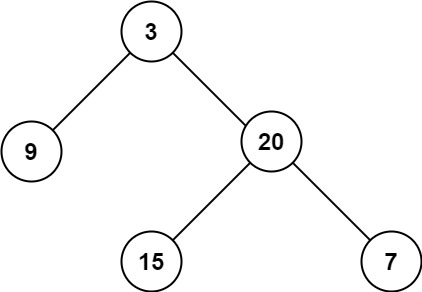
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解法
递归解法
核心思想:求最大深度,其实就是求root的高度。求高度使用的是后序遍历,左右中
左右中,最后处理中,才能递归把左和右的结果,拿来给中用。为什么不使用前序遍历,中左右,来直接求深度呢?因为无法让下层节点利用上层节点来递归
递归实现:
- 输入参数:Optional[node]
- 输出参数:int(高度)
- 结束条件:如果传入的node为空,则返回0(最下层元素的高度是1,那么None的就是0)
- 单层核心逻辑:递归求左右子节点的高度,然后将较大的值加上1,就是当前节点的高度
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: return self.getHeight(root) def getHeight(self, node: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: # 终止条件 if node is None: return 0 # 单层核心逻辑 # 以下四条语句,可以合并为最后一条语句 # left_height = self.getHeight(node.left) # right_height = self.getHeight(node.right) # cur_height = max(left_height, right_height) + 1 # return cur_height return 1 + max(self.getHeight(node.left), self.getHeight(node.right))